Seattle residents can now breathe easier; no more racist firemen
/Seattle firemen now drilled on Ibram Kendi before promotion to top jobs.
Of all the jobs in a standard fire department, a lieutenant’s is among the most difficult. When a fire truck approaches a blaze, the lieutenant decides how to tackle it—what windows to breach, which floors to prioritize, and how best to deploy the truck’s three or four firefighters against a shifting, inanimate enemy.
To see if they’re up to snuff, most departments administer a written test, typically multiple-choice, to prospective lieutenants. Candidates must score above a cut-off to be considered for the job, with higher scores increasing the odds of promotion. The exam, which covers a litany of topics from building construction to medical techniques, is designed to ensure that the people making life-and-death decisions know the bare minimum to make them well.
So firefighters in Seattle, Washington, were surprised when their department’s lieutenant exam focused almost as much on social justice as on firefighting.
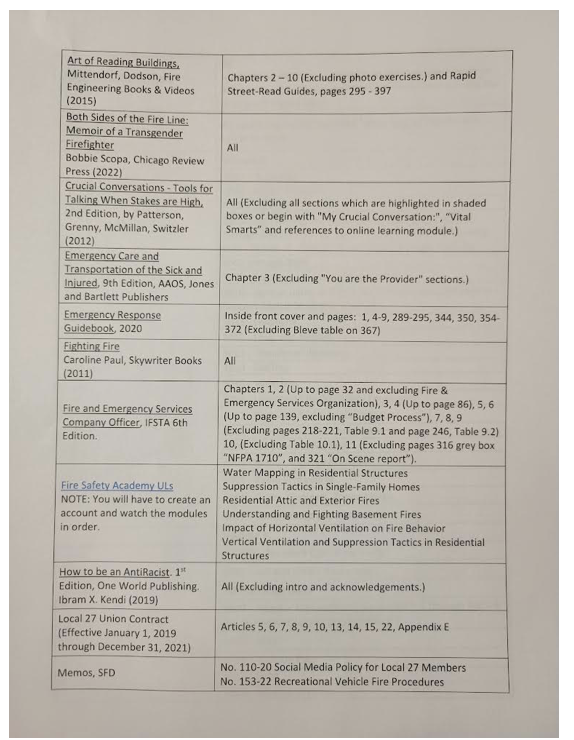
The test, which has both written and oral components, is based on a list of texts assigned by the Seattle Department of Human Resources—including, as of this year, How To Be An Antiracist by Ibram X. Kendi and Both Sides of the Fire Lane: Memoirs of a Transgender Firefighter by Bobbie Scopa, according to a copy of the exam bibliography obtained by the Washington Free Beacon.
Along with A Leader’s Guide to Unconscious Bias and Fighting Fire, a memoir by a female firefighter, the books about race and gender span over 800 pages—a large fraction of the total study material.
The exam is part of a much larger effort to diversify a department that, as Seattle fire chief Harold Scoggins lamented last year, is "overwhelmingly" white men. Those efforts, critics say, have made the promotion process more about ideology and less about merit, politicizing a public service where competence can mean the difference between life and death.
In fact, in 2021, local officials including Scoggins commissioned a report on diversity in the fire service. One of its recommendations: avoid tests that "rely heavily on knowledge of firefighting."
"[T]ests that focus on how well applicants know the system and the job tend to favor those who make up the overwhelming majority of the fire service workforce, white men," the report says. "Questions that ask more about the candidate’s character and values, rather than knowing the ins and outs of the job, can be beneficial in advancing more women and people of color."
Seattle appears to have taken that advice.
An upcoming test for fireboat engineers, who operate the pumps and nozzles used to douse coastal fires, will quiz candidates on Robin DiAngelo’s Is Everyone Really Equal?: An Introduction to Key Concepts in Social Justice Education, according to the exam bibliography. The fire captains exam likewise assigns DiAngelo’s book—along with handouts on the "structural interplay between all oppressions"—while the exam for battalion chiefs assigns the 2021 report on fire service diversity.
Scoggins did not respond to a request for comment.
Seattle’s tests are an outlier. In most cities, even Democratic strongholds like Boston and New Haven, written fire exams test only tactical knowledge. But in Seattle, where Scoggins himself helped protesters seal off the Capitol Hill Autonomous Zone in the wake of George Floyd’s death, promotions hinge on mastering these ideological tomes.